Risk Factors and Causes of Diabetic Foot Complications
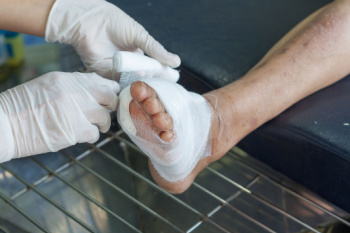
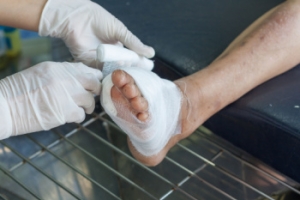
Diabetic foot complications are a significant concern for people with diabetes. Problems arise from peripheral neuropathy, poor circulation, and increased susceptibility to infections. Peripheral neuropathy, affecting up to 70 seventy percent of diabetic patients, leads to loss of sensation in the feet. This makes injuries and infections more likely to go unnoticed and untreated. Poor blood circulation due to damaged blood vessels makes the situation worse by impeding the healing process. This contributes to the development of non-healing ulcers and, in severe cases, gangrene. Complications from diabetes result in serious outcomes in up to a quarter of diabetic patients, and, alarmingly, contribute to approximately 70 percent of leg amputations in diabetics patients. Comprehensive foot care programs have shown to significantly decrease amputation rates. A podiatrist can provide early diagnosis and intervention, manage infections, and recommend proper footwear to prevent injuries. If you are suffering from foot problems due to diabetes, it is suggested that you make a podiatrist a part of your medical team and schedule regular checkups of your feet.
Diabetic foot care is important in preventing foot ailments such as ulcers. If you are suffering from diabetes or have any other concerns about your feet, contact Lesly Honore, MD, DPM from New York. Our doctor can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetes affects millions of people every year. The condition can damage blood vessels in many parts of the body, especially the feet. Because of this, taking care of your feet is essential if you have diabetes, and having a podiatrist help monitor your foot health is highly recommended.
The Importance of Caring for Your Feet
- Routinely inspect your feet for bruises or sores.
- Wear socks that fit your feet comfortably.
- Wear comfortable shoes that provide adequate support.
Patients with diabetes should have their doctor monitor their blood levels, as blood sugar levels play such a huge role in diabetic care. Monitoring these levels on a regular basis is highly advised.
It is always best to inform your healthcare professional of any concerns you may have regarding your feet, especially for diabetic patients. Early treatment and routine foot examinations are keys to maintaining proper health, especially because severe complications can arise if proper treatment is not applied.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our office located in Hempstead, NY . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
How to Care for Diabetic Foot
Millions of people are affected by diabetes each year. Diabetes damages blood vessels in all parts of the body, especially the feet. The legs and feet may develop slow blood flow, which causes neuropathy, or nerve damage. Once a diabetic patient develops neuropathy, it is important that the feet are well taken care of. Otherwise, the lower limbs may have to be amputated. This only happens in drastic cases, but it shows how seriously diabetic foot care should be taken.
It is very important to always wash and dry the feet thoroughly, especially in between the toes, if you’re a diabetic. Secondly, examining your feet and toes for redness or sores must be done, even if you do not feel pain. You may also want to examine your feet from the bottom. Try to avoid wearing colored socks to prevent infections that may occur from the dye. Well-fitting socks are also highly recommended.
A diabetic’s physician should always monitor their blood levels to test how well blood sugars are being maintained. In addition to giving advice about everyday eating habits and foot care, a physician may prescribe medicine to help with the diabetic patient’s neuropathy. It is also advised to see a podiatrist if experiencing any feet conditions. Toenails may also need to be taken care of by a podiatrist. This prevents patients from cutting too deeply around their cuticles, which can lead to infection.
A person can take care of their feet at home by following the instructions of their physician. Using creams on one’s feet is also an effective way to heal dryness. Proceed with caution when using tools to remove calluses, as severe diabetics may not be able to feel pain on their feet. If any complications arise do not hesitate to contact a podiatrist.
On a daily basis, diabetic feet must be checked. If you are ever concerned about something, contact your health care professional. You never want to wait until a wound becomes too severe to treat. If left untreated, gangrene may develop. Gangrene is a serious infection that can lead to sepsis or amputation. It is also important for diabetics to be on the lookout for ulcers. Ulcers are sores that develop from tissue loss on the skin. They can be quite painful and require intensive treatment. Early treatment and everyday inspection are imperative to staying healthy.
Stretches Can Help the Feet

Standing for prolonged periods of time can cause aches and pains in your feet and lower limbs. In addition to wearing comfortable shoes and taking breaks to sit and walk around, one other way that you can prevent or relieve pain is to stretch. A lunging calf stretch can help prevent cramping in the calf muscles, plantar fasciitis, and other foot problems. It can also promote circulation. To do this stretch, stand one step away from a wall and place both palms flat against it. Step your left foot back and bend your right knee into a lunge. Keep your toes pointing forward and slowly push your left heel toward the ground until you feel a stretch in your calf. Hold and then repeat on the opposite foot. To learn more about the benefits of stretching your feet, it’s suggested that you consult with a podiatrist.
Stretching the feet is a great way to prevent injuries. If you have any concerns with your feet consult with Lesly Honore, MD, DPM from New York. Our doctor will assess your condition and provide you with quality foot and ankle treatment.
Stretching the Feet
Being the backbone of the body, the feet carry your entire weight and can easily become overexerted, causing cramps and pain. As with any body part, stretching your feet can serve many benefits. From increasing flexibility to even providing some pain relief, be sure to give your feet a stretch from time to time. This is especially important for athletes or anyone performing aerobic exercises, but anyone experiencing foot pain or is on their feet constantly should also engage in this practice.
Great ways to stretch your feet:
- Crossing one leg over the others and carefully pull your toes back. Do 10-20 repetitions and repeat the process for each foot
- Face a wall with your arms out and hands flat against the wall. Step back with one foot and keep it flat on the floor while moving the other leg forward. Lean towards the wall until you feel a stretch. Hold for 30 seconds and perform 10 repetitions for each foot
- Be sure not to overextend or push your limbs too hard or you could risk pulling or straining your muscle
Individuals who tend to their feet by regular stretching every day should be able to minimize foot pain and prevent new problems from arising.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office located in Hempstead, NY . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
How to Care for Diabetic Foot
Millions of people are affected by diabetes each year. Diabetes damages blood vessels in all parts of the body, especially the feet. The legs and feet may develop slow blood flow, which causes neuropathy, or nerve damage. Once a diabetic patient develops neuropathy, it is important that the feet are well taken care of. Otherwise, the lower limbs may have to be amputated. This only happens in drastic cases, but it shows how seriously diabetic foot care should be taken.
It is very important to always wash and dry the feet thoroughly, especially in between the toes, if you’re a diabetic. Secondly, examining your feet and toes for redness or sores must be done, even if you do not feel pain. You may also want to examine your feet from the bottom. Try to avoid wearing colored socks to prevent infections that may occur from the dye. Well-fitting socks are also highly recommended.
A diabetic’s physician should always monitor their blood levels to test how well blood sugars are being maintained. In addition to giving advice about everyday eating habits and foot care, a physician may prescribe medicine to help with the diabetic patient’s neuropathy. It is also advised to see a podiatrist if experiencing any feet conditions. Toenails may also need to be taken care of by a podiatrist. This prevents patients from cutting too deeply around their cuticles, which can lead to infection.
A person can take care of their feet at home by following the instructions of their physician. Using creams on one’s feet is also an effective way to heal dryness. Proceed with caution when using tools to remove calluses, as severe diabetics may not be able to feel pain on their feet. If any complications arise do not hesitate to contact a podiatrist.
On a daily basis, diabetic feet must be checked. If you are ever concerned about something, contact your health care professional. You never want to wait until a wound becomes too severe to treat. If left untreated, gangrene may develop. Gangrene is a serious infection that can lead to sepsis or amputation. It is also important for diabetics to be on the lookout for ulcers. Ulcers are sores that develop from tissue loss on the skin. They can be quite painful and require intensive treatment. Early treatment and everyday inspection are imperative to staying healthy.
Managing Your Non-Diabetic Foot Infection
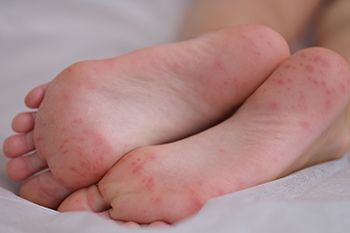
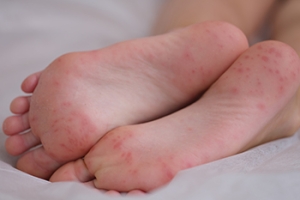
Non-diabetic foot infections can arise from various sources, including cuts, puncture wounds, or fungal infections. Symptoms often include redness, swelling, and pain, potentially accompanied by drainage or fever if severe. Causes range from minor injuries to exposure in moist environments. Immediate treatment involves cleaning the affected area with mild soap and water, applying an antibiotic ointment, and covering with a clean bandage. Keeping weight off the affected foot and elevating it can aid healing. It is important to monitor for worsening symptoms or signs of infection. For persistent infections, particularly those spreading or not responding to initial care, seeking prompt evaluation by a podiatrist is key. This type of doctor can assess the infection's severity, provide stronger antibiotics or drainage procedures if necessary, and ensure comprehensive care to promote healing and prevent complications. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is suggested you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist for specialized treatment.
Wound care is an important part in dealing with diabetes. If you have diabetes and a foot wound or would like more information about wound care for diabetics, consult with Lesly Honore, MD, DPM from New York. Our doctor will assess your condition and provide you with quality foot and ankle treatment.
What Is Wound Care?
Wound care is the practice of taking proper care of a wound. This can range from the smallest to the largest of wounds. While everyone can benefit from proper wound care, it is much more important for diabetics. Diabetics often suffer from poor blood circulation which causes wounds to heal much slower than they would in a non-diabetic.
What Is the Importance of Wound Care?
While it may not seem apparent with small ulcers on the foot, for diabetics, any size ulcer can become infected. Diabetics often also suffer from neuropathy, or nerve loss. This means they might not even feel when they have an ulcer on their foot. If the wound becomes severely infected, amputation may be necessary. Therefore, it is of the upmost importance to properly care for any and all foot wounds.
How to Care for Wounds
The best way to care for foot wounds is to prevent them. For diabetics, this means daily inspections of the feet for any signs of abnormalities or ulcers. It is also recommended to see a podiatrist several times a year for a foot inspection. If you do have an ulcer, run the wound under water to clear dirt from the wound; then apply antibiotic ointment to the wound and cover with a bandage. Bandages should be changed daily and keeping pressure off the wound is smart. It is advised to see a podiatrist, who can keep an eye on it.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office located in Hempstead, NY . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Wound Care
Diabetics must be wary of all wounds, regardless of depth or size. Diabetes, a chronic disease in which the body cannot properly use glucose the way it normally would, causes various complications that make wounds difficult to heal. Nerve damage or neuropathy will cause diabetics to have trouble feeling the pain of a blister or cut until the condition has significantly worsened or become infected. A diabetic’s weakened immune system can make even the most minor of wounds easily susceptible to infection. Diabetics are also more prone to developing narrow, clogged arteries, and are therefore more likely to develop wounds.
Wounds should be taken care of immediately after discovery, as even the smallest of wounds can become infected if enough bacteria build up within the wound. To remove dirt, wounds should be first rinsed under running water only. Soap, hydrogen peroxide, or iodine can irritate the injury and should be avoided. To prevent infection, apply antibiotic ointment to the wound and cover it with a bandage. The bandage should be changed daily. The skin around the wound may be cleaned with soap.
To prevent further exacerbation, see a doctor—especially if you have diabetes. Minor skin conditions can become larger problems if not properly inspected. As the wound heals, make sure to avoid applying pressure to the affected area.
Causes of Ankle Pain in Runners

Ankle pain, which plagues many runners, stems from the repetitive stress placed on the joints with every step. Runners take approximately 1,700 steps per mile, each one contributing to the cumulative strain on their ankles. The primary causes of ankle pain in runners include ankle sprains, strains, tendonitis, and stress fractures. Ankle sprains involve stretched or torn ligaments, resulting in pain, swelling, and difficulty in moving the ankle. Strains, which are injuries to the tendons, can cause pain, muscle spasms, and cramping. Tendonitis, the inflammation or irritation of a tendon, is often triggered by overuse, wearing improper footwear, repetitive motion, and conditions like low arches or flat feet. Symptoms can include a dull ache, tenderness, and limited swelling. Stress fractures, which are tiny cracks in the bones caused by repetitive force and overuse, can result from excessive mileage, in addition to sudden increases in running distance and changes in running surfaces. Symptoms include worsening pain that diminishes with rest and limited swelling. If you are experiencing ankle pain from running, it is suggested that you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist for an exam and treatment options.
Ankle pain can be caused by a number of problems and may be potentially serious. If you have ankle pain, consult with Lesly Honore, MD, DPM from New York. Our doctor will assess your condition and provide you with quality foot and ankle treatment.
Ankle pain is any condition that causes pain in the ankle. Due to the fact that the ankle consists of tendons, muscles, bones, and ligaments, ankle pain can come from a number of different conditions.
Causes
The most common causes of ankle pain include:
- Types of arthritis (rheumatoid, osteoarthritis, and gout)
- Ankle sprains
- Broken ankles
- Achilles tendonitis
- Achilles tendon rupture
- Stress fractures
- Bursitis
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome
- Plantar fasciitis
Symptoms
Symptoms of ankle injury vary based upon the condition. Pain may include general pain and discomfort, swelling, aching, redness, bruising, burning or stabbing sensations, and/or loss of sensation.
Diagnosis
Due to the wide variety of potential causes of ankle pain, podiatrists will utilize a number of different methods to properly diagnose ankle pain. This can include asking for personal and family medical histories and of any recent injuries. Further diagnosis may include sensation tests, a physical examination, and potentially x-rays or other imaging tests.
Treatment
Just as the range of causes varies widely, so do treatments. Some more common treatments are rest, ice packs, keeping pressure off the foot, orthotics and braces, medication for inflammation and pain, and surgery.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office located in Hempstead, NY . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Bunions
A bunion is an enlargement of the base joint of the toe that connects to the foot, often formed from a bony growth or a patch of swollen tissues. It is caused by the inward shifting of the bones in the big toe, toward the other toes of the foot. This shift can cause a serious amount of pain and discomfort. The area around the big toe can become inflamed, red, and painful.
Bunions are most commonly formed in people who are already genetically predisposed to them or other kinds of bone displacements. Existing bunions can be worsened by wearing improperly fitting shoes. Trying to cram your feet into high heels or running or walking in a way that causes too much stress on the feet can exacerbate bunion development. High heels not only push the big toe inward, but shift one's body weight and center of gravity towards the edge of the feet and toes, expediting bone displacement.
A podiatrist knowledgeable in foot structure and biomechanics will be able to quickly diagnose bunions. Bunions must be distinguished from gout or arthritic conditions, so blood tests may be necessary. The podiatrist may order a radiological exam to provide an image of the bone structure. If the x-ray demonstrates an enlargement of the joint near the base of the toe and a shifting toward the smaller toes, this is indicative of a bunion.
Wearing wider shoes can reduce pressure on the bunion and minimize pain, and high heeled shoes should be eliminated for a period of time. This may be enough to eliminate the pain associated with bunions; however, if pain persists, anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. Severe pain may require an injection of steroids near the bunion. Orthotics for shoes may be prescribed which, by altering the pressure on the foot, can be helpful in reducing pain. These do not correct the problem; but by eliminating the pain, they can provide relief.
For cases that do not respond to these methods of treatment, surgery can be done to reposition the toe. A surgeon may do this by taking out a section of bone or by rearranging the ligaments and tendons in the toe to help keep it properly aligned. It may be necessary even after surgery to wear more comfortable shoes that avoid placing pressure on the toe, as the big toe may move back to its former orientation toward the smaller toes.
Understanding Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
 Tarsal tunnel syndrome is a condition characterized by the compression of the tibial nerve as it travels through the tarsal tunnel, a narrow space on the inside of the ankle. This tunnel houses several vital structures, including the tibialis posterior tendon, the flexor digitorum longus tendon, and the posterior tibial artery and vein. When the tibial nerve is compressed, it can lead to pain, tingling, and numbness in the foot. The tibialis posterior tendon helps support the arch of the foot, while the flexor digitorum longus tendon aids in flexing the toes. The posterior tibial artery and vein are essential for blood circulation to the foot. If you have pain in this part of your foot, it is suggested that you consult a podiatrist who can diagnose and treat tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is a condition characterized by the compression of the tibial nerve as it travels through the tarsal tunnel, a narrow space on the inside of the ankle. This tunnel houses several vital structures, including the tibialis posterior tendon, the flexor digitorum longus tendon, and the posterior tibial artery and vein. When the tibial nerve is compressed, it can lead to pain, tingling, and numbness in the foot. The tibialis posterior tendon helps support the arch of the foot, while the flexor digitorum longus tendon aids in flexing the toes. The posterior tibial artery and vein are essential for blood circulation to the foot. If you have pain in this part of your foot, it is suggested that you consult a podiatrist who can diagnose and treat tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Tarsal tunnel syndrome can be very uncomfortable to live with. If you are experiencing tarsal tunnel syndrome, contact Lesly Honore, MD, DPM of New York. Our doctor can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tarsal tunnel syndrome, which can also be called tibial nerve dysfunction, is an uncommon condition of misfiring peripheral nerves in the foot. The tibial nerve is the peripheral nerve in the leg responsible for sensation and movement of the foot and calf muscles. In tarsal tunnel syndrome, the tibial nerve is damaged, causing problems with movement and feeling in the foot of the affected leg.
Common Cause of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Involves pressure or an injury, direct pressure on the tibial nerve for an extended period of time, sometimes caused by other body structures close by or near the knee.
- Diseases that damage nerves, including diabetes, may cause tarsal tunnel syndrome.
- At times, tarsal tunnel syndrome can appear without an obvious cause in some cases.
The Effects of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Different sensations, an afflicted person may experience pain, tingling, burning or other unusual sensations in the foot of the affected leg.
- The foot muscles, toes and ankle become weaker, and curling your toes or flexing your foot can become difficult.
- If condition worsens, infections and ulcers may develop on the foot that is experiencing the syndrome.
A physical exam of the leg can help identify the presence of tarsal tunnel syndrome. Medical tests, such as a nerve biopsy, are also used to diagnose the condition. Patients may receive physical therapy and prescriptive medication. In extreme cases, some may require surgery.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our office located in Hempstead, NY . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is a condition in which there is a compression of the posterior tibial nerve. The posterior tibial nerve runs along the inside of the ankle into the foot. Tarsal tunnel syndrome is named for the tarsal tunnel, which is a thin space along the inside of the ankle beside the ankle bones. This space contains various nerves, arteries, and tendons, and includes the posterior tibial nerve. The tibial nerve is the peripheral nerve in the leg responsible for sensation and movement of the foot and calf muscles. In tarsal tunnel syndrome the tibial nerve is compressed, causing tingling or burning, numbness, and pain.
Common causes of tarsal tunnel syndrome involve pressure or an injury. Injuries that produce inflammation and swelling in or around the tunnel may place pressure on the posterior tibial nerve. Direct pressure on the tibial nerve for an extended period of time, sometimes caused by other body structures close by or trauma to the tibial nerve, can result in tarsal tunnel syndrome. Diseases that damage nerves, such as diabetes or arthritis, may cause tarsal tunnel syndrome. Those with flat feet are at risk for developing the condition, as the extra pressure and strain placed on the foot may compress the posterior tibial nerve.
Feeling different sensations in the foot at different times is a common symptom of tarsal tunnel syndrome. An afflicted person may experience pain, tingling, burning or other unusual sensations in the foot of the affected leg. Symptoms are primarily felt on bottom of the foot and/or the inside of the ankle. Symptoms can appear suddenly and may occur due to overuse of the foot.
To diagnose tarsal tunnel syndrome, your podiatrist may examine the foot and tap the posterior tibial nerve to see if symptoms surface. He or she may also order an MRI to determine if a mass is present.
Treating tarsal tunnel syndrome will depend on the decision of your podiatrist. Multiple options are available, however, and can include rest, ice, immobilization, oral medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), physical therapy, injection therapy, orthotics, supportive shoes, braces, and surgery.